Alignment
Wheel alignment consists of adjusting the angles of the wheels so that they are perpendicular to the ground and parallel to each other. The purpose of these alignments is to maximize the tyres life, fuel efficiency and ensure that the vehicle tracks straight and true when driving along a straight and level road. Severe impacts (hitting potholes or curbs) and worn suspension parts are the leading causes of misalignment.
All Season Tyres
Tyres designed to provide good traction in a wide variety of road conditions, including wet, dry and mud and snow. This design also limits the tyre’s performance in extreme conditions, or when compared to tyres built for a particular category.
Aspect Ratio
A term that describes a tyre’s height-to-width proportion. If a tyre’s sidewall height were 65% of its width, its aspect ratio would be 65. In the tyre size expressed as 205/65-15, the number 65 is the aspect ratio.
Balance
The state in which a tyre and wheel assembly spins with all its weight distributed equally. Wheel Balancing allows the tyres and wheels to spin without causing any vibrations. This is done by checking for any heavy spots on the wheel-tire combination and compensating for it by placing a measured lead weight on the opposite site of the wheel from where the heavy spot is.
Bar
This is a unit of measurement for air pressure within tyres.
Bead
A round hoop of steel wires, wrapped or reinforced by steel cords, placed at the very inside of the tyre's diameter.
Bias Ply Tyre
A tyre manufactured such that the plies are laid at alternate angles less than 90 degrees to the centerline of the tread. These criss-cross plies give the tyre its strength, but generate heat during operation and limit the tyre's wear and performance.
Carcass
The tyre body beneath the tread and sidewalls; also called the casing.
Contact Patch
The portion of the tread that in touching the road during operation.
Cord
The strands of material forming the plies or layers of tyre. Cords may be made from fiberglass, rayon, nylon, polyester or steel.
DOT Markings
Each tyre has a required Department of Transportation number imprinted on at least one of its sidewalls. That number begins with the letters "DOT" and may contain up to 12 additional numbers and letters. The first and last digits are the most important for the tyre owner. The first two letters/numbers identify the manufacturer of the tyres. The first two digits represent the week of production and the last two digits represent the last two digits of the year of production. So, 5114 as the last four numbers indicates that the tyre was produced in the 51st week of the year 2014.
Footprint
The full portion of the tyre that makes contact with the surface of the road.
Friction
The resistance of the tyre tread as it moves on the road; this is the force that causes the tyre to grip to the road.
Groove
The space between two adjacent tread ribs; also called tread grooves.
Hydroplaning
A skimming effect caused by tyres losing contact with a surface covered by water. This results in loss of grip
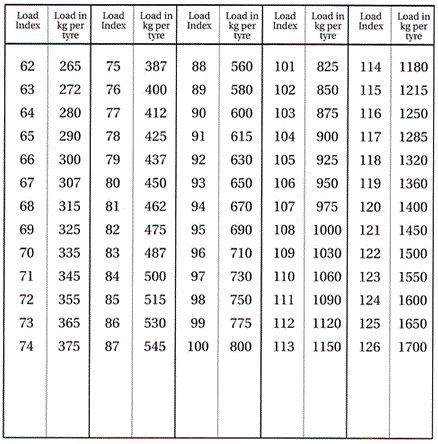
Load Index
An assigned number ranging from 0 to 279 that corresponds to the load carrying capacity of the tyre.
M+S, M/S or M & S
Indicates that a tyre can reach particular standards for performance in mud and snow conditions.
Max. Inflation Pressure
The maximum air pressure to which a cold tyre may be inflated; found stamped onto the tyre's sidewall.
OE and OEM
OE means "Original Equipment" and refers to the tyres included with a new vehicle at the time of purchase. The vehicle's manufacturer selects these tyres to provide the optimal performance based on the performance characteristics of the vehicle. "OEM" stands for "Original Equipment Manufacturer."
Overall Diameter
The diameter of an inflated tyre without any load.
Overall Width
The distance between a tyre's outside sidewalls, including lettering and designs.
P Metric
Uniform designation of tyre sizes in metric measurements originally introduced by American tyre manufacturers in 1977. Commonly called "P-metric series." A typical P-metric tyre size is P215/70R-15.
Placard
A small label typically located on the edge of the driver's door or inside the glove compartment of a vehicle. A placard contains information on the vehicle such as the manufacturer's recommended tyre inflation pressure.
Plus-Sizing
A practice allowing drivers to customize the appearance and performance of their vehicle by mounting lower profile tyres on larger diameter wheels. One-inch greater wheel diameter is referred to as plus-one, two inches is plus-two... and so on. Using a lower profile tyre with a greater diameter rim allows the overall diameter to remain about the same.
Ply
A rubber-coated layer of fabric containing cords that run parallel to each other; extends from bead to bead and goes between the inner-liner and belts of tread.
Ply Rating
This indicates the load carrying capacity of the tyre in terms of its construction. A "C" indicates the tyre has a 6-ply load carrying capacity. The tyre is not actually built with 6 plies, but contains one or two plies of equivalent strength. A "D" is an 8-ply rating, and an "E" is a 10-ply rating. If there is no letter, the tyre has a standard 4-ply rating.
PSI
Pounds per Square Inch. This is the standard unit of measurement for air pressure within tyres.
Radial Ply
Tyre construction where the cords in the body run at 90 degrees to the centerline of the tread.
Rim Width
Distance between the two opposite inside edges of the rim flanges.
Rolling Resistance
The force required to keep a tyre moving at a constant speed. The lower the rolling resistance, the less energy needed to keep a tyre moving.
Rotation
Moving tyres from side to side or front to rear on a vehicle in a prescribed pattern to achieve uniform wear on all tyres. Rotations should be performed regularly every 10,000 KMS
Shoulder
The part of a tyre where the sidewall and tread meet. Certain tyre design features shoulder blocks for better traction.
Sidewall
The part of the tyre between the tread and the bead.
Size
An expression that defines a particular tyre in terms of its width, height, rim diameter, aspect ratio and construction type. 225/50-R17 expresses tyre size using the metric system.
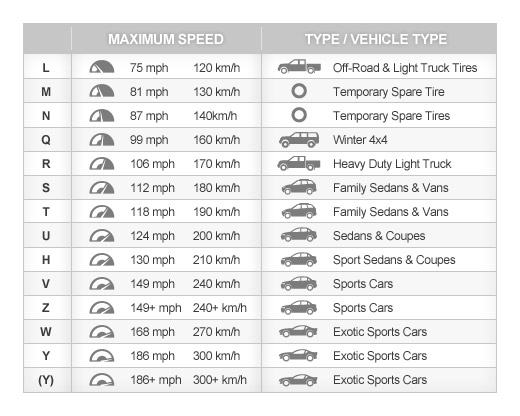
Speed Rating
Speed rating represents the maximum speed your tyre is capable of maintaining. It is always represented by a letter. Take a 195/65R15 87S tyre- The Speed rating here is represents by the Letter S which translates to the tyre’s ability to maintain speeds of up to 180 km/h.
Tyre Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS)
TPMS is an automated system that monitors the air pressure in a vehicle's tyres. When air pressure in one or more tyres drops 25 percent or more below the correct pressure, a warning alerts the driver.
Traction
The friction between a tyre and the road surface; the amount of grip provided.
Tread
The part of the tyre that comes into contact with the road. The tread type is distinguished by the design of its ribs and grooves
Tread Depth
The distance measured in the major tread groove nearest the centerline of the tyre from the base of the groove to the top of the tread.
Treadwear Indicator
Narrow bands, sometimes called "wear bars", that appear across the tread when 2/32" of tread remains.
Tread Width
The width of a tyre's tread.
UTQG (Uniform Tyre Quality Grading)
A tyre information system that provides consumers with ratings for a tyre's traction (AA to C) and temperature (A to C)
Valve
A device mounted in the wheel that lets air in or out of the tyre. Valves include caps to keep out dirt and moisture and a valve to prevent air from escaping.